Injectable solutions are pharmaceutical products that have different compositions, each used for a specific disease. Injectable solutions contain electrolytes, amino acids, carbohydrates, and other components. The chemical composition and osmotic concentration of injectable solutions are important in their classification, and they are categorized based on these criteria.
Currently, the production line of injectable solutions at the knowledge-based company Bayerpaul PharmaTech manufactures more than 12 different injectable products. In addition to supplying domestic markets, a portion of these products is also exported.
Magnesium sulfateMagnesium sulfate is an active ingredient with a vital role in the body, regulating the nervous system and blood, as well as possessing anti-arrhythmic and anti-ischemic effects. This medication is an injectable solution used for magnesium deficiency and for preventing and controlling seizures in patients with severe preeclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy). | 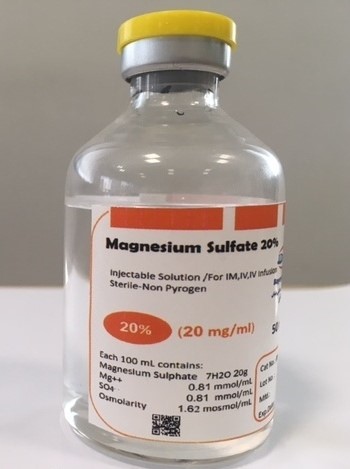 |
DextroseGlucose is a type of sugar that is essential for the body’s normal functioning as a critical source of energy. Intravenous glucose infusion is used to reverse coma caused by low blood sugar levels. It is also utilized as an energy source or during times of reduced carbohydrate intake. Additionally, it can be employed for reducing intracranial pressure or cerebral edema. |  |
Potassium chloridePotassium chloride is used as a medication for treating and preventing low blood potassium levels. Decreased potassium in the blood may occur due to vomiting, diarrhea, or certain medications. Concentrated solutions should be diluted before use. This solution should be administered slowly intravenously or orally. |  |
Sodium chlorideSodium is the primary cation in extracellular fluid and plays a crucial role in controlling water distribution, fluid and electrolyte balance, and osmotic pressure of body fluids. Chloride, the predominant extracellular anion, primarily contributes to maintaining the physiological state of sodium cation in preserving cellular acid-base balance, isotonicity, and electrodynamic properties of cells. Therefore, intravenous injection of sodium chloride (0.9%) serves as a valuable source of water and electrolytes. | |
LidocaineLidocaine, also known as lignocaine and xylocaine, is a medication used for local tissue anesthesia (local anesthetic). It is also used for the treatment of ventricular tachycardia and nerve block. Lidocaine, when combined with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine), enhances the anesthetic effect to prevent bleeding and prolong the duration of anesthesia. When lidocaine is administered by injection, anesthesia typically begins within four minutes and can last from 30 minutes to 3 hours. Lidocaine formulations can also be directly applied to the skin or mucous membranes to induce anesthesia in that area. |  |


